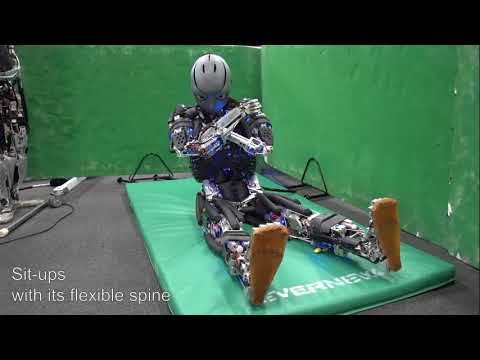
Current and previous single-legged hopping robots are energetically tethered and lack portability. Here, we present the design and control of an untethered, energetically autonomous single-legged hopping robot. The thrust-producing mechanism of the robot’s leg is an actuated prismatic joint, called a linear elastic actuator in parallel (LEAP). The LEAP mechanism comprises a voice coil actuator in parallel with two compression springs, which gives our robot passive compliance. An actuated gimbal hip joint is realized by two standard servomotors. To control the robot, we adapt Raibert’s hopping controller, and find we can maintain balance roughly in-place for up to approx. 7 seconds (19 hops) while continuously hopping.